Models
Our research involves the development of models in a broad sense, including models of the Earth's interior, ice sheets, and seismic sources. Below you can find a collection of such models with download links.
Hot models (> 0 °C)
- Collaborative Seismic Earth Model: Generation 2 (CSEM2)
- REVEAL: Global-scale full-waveform inversion model
- FWI of the African Plate
- Long-wavelength Earth model (LOWE)
- Collaborative Seismic Earth Model: Generation 1(CSEM1)
Cool models (< 0 °C)
Stormy models
Collaborative Seismic Earth Model: Generation 2
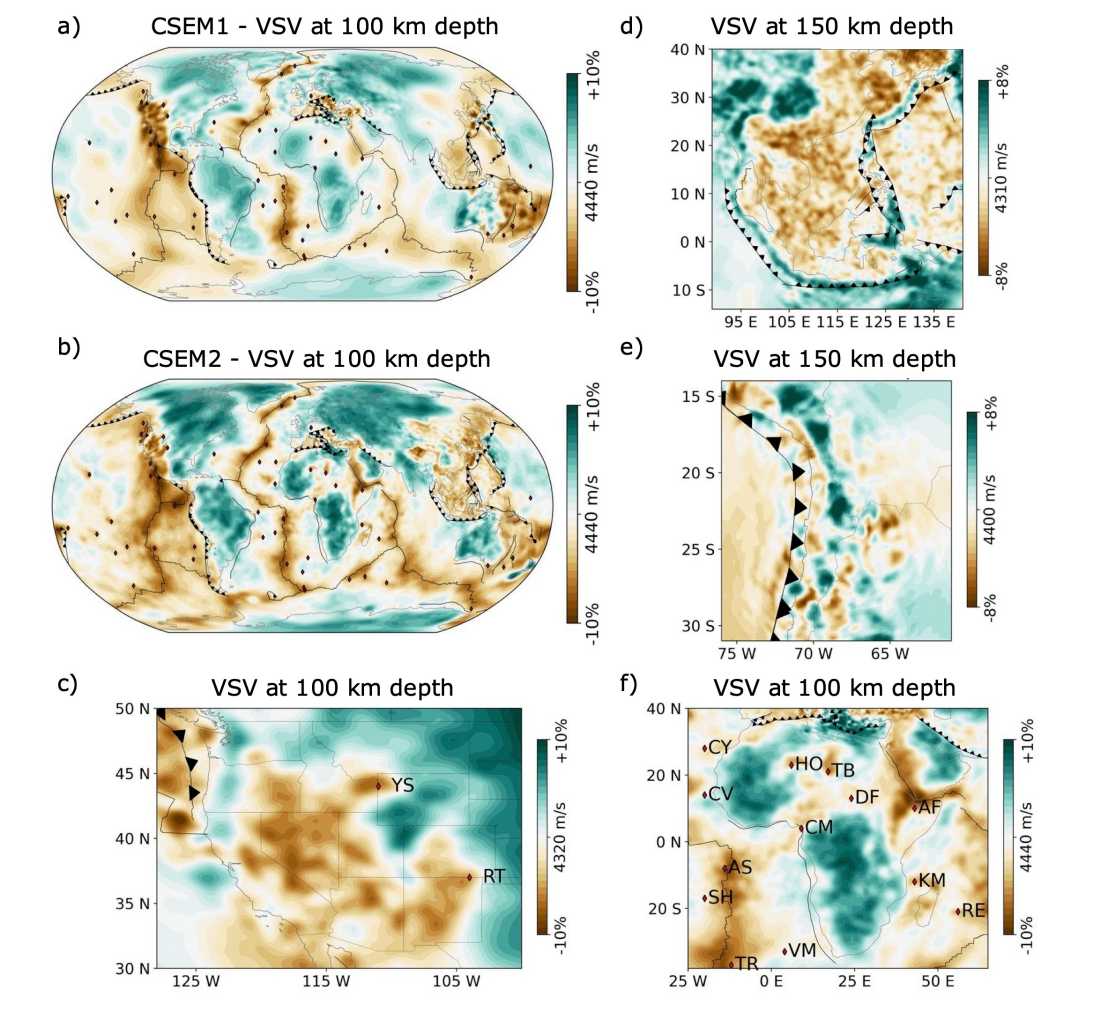
Geological interpretations, earthquake source inversions and ground motion modeling, among other applications, require models that jointly resolve crustal and mantle structure. With the second generation of the Collaborative Seismic Earth Model (CSEM2), we present a global multi-resolution tomographic Earth model that serves this purpose. The model evolves through successive regional- and global-scale refinements. While the first generation aggregated regional models, with this study, we ensure consistency between all individual submodels, resulting in a model that accurately explains wave propagation across scales. Recent regional tomographic models were incorporated, comprising continental-scale inversions for Asia and Africa, as well as regional inversions for the Western US, Central Andes, Iran, and Southeast Asia. Across all regional refinements, over 793,000 source-receiver pairs contributed. Moreover, the long-wavelength Earth model (LOWE) introduces large-scale structures outside of pre-existing local refinements. A full-waveform inversion for global anisotropic P-and S-wave speed structure over a total of 194 iterations with a minimum period of 50 s on a large data set of 1 hr of waveform data from 2,423 earthquakes and over 6 million source-receiver pairs ensures that regional updates in the crust and uppermost mantle translate into updates of deeper, global-scale structure. To test the performance of CSEM2, we evaluate waveform fits between observed and synthetic seismograms at 50 s for an independent data set on the global scale, and on the regional scale for lower periods. We accurately simulate waveforms within and across regional refinements, maintaining the original resolution of the submodels embedded in the global framework.
Resources
Several regional submodels can be downloaded in netcdf format and plotted with a Download Python Jupyter notebook:
Publication
external page The Collaborative Seismic Earth Model: Generation 2
REVEAL: Global-scale full-waveform inversion model
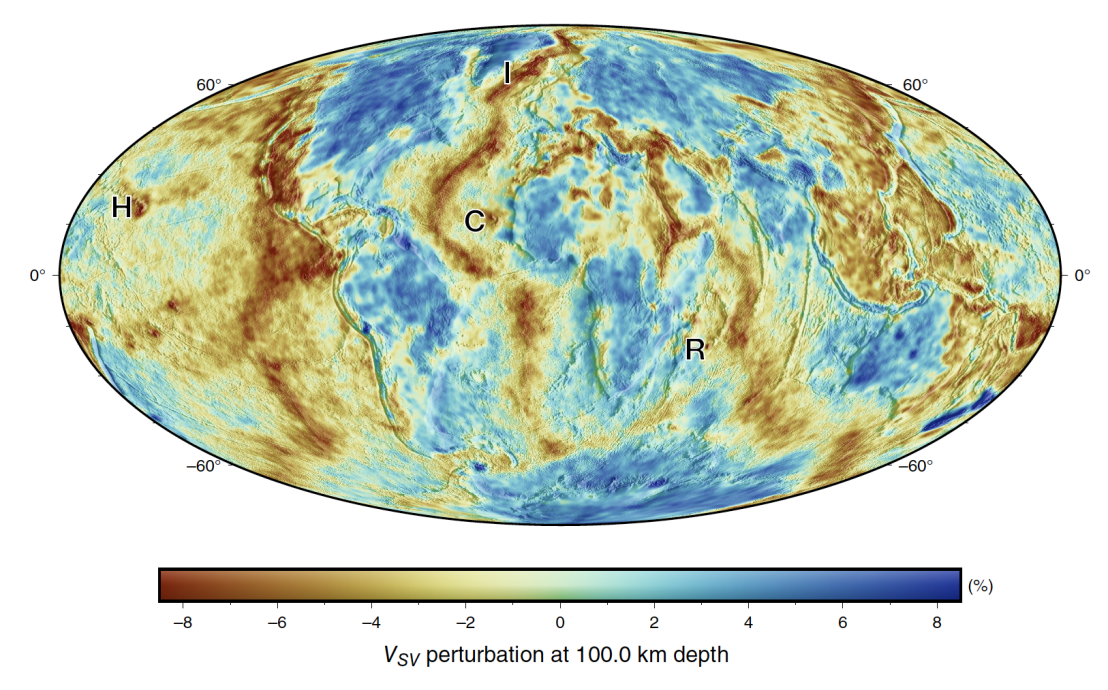
We present REVEAL, a global-scale, transversely isotropic full-waveform inversion model. REVEAL builds upon the earlier construction of the long-wavelength Earth (LOWE) model by lowering the minimum period from 100 to 33 s and by more than doubling the number of included earthquakes to 2366. In the course of 305 quasi-Newton iterations, REVEAL assimilated a total of 6,005,727 unique three-component waveforms. The inversion method rests on the combination of a stochastic mini-batch optimization and wavefield-adapted spectral-element meshes. Although the former naturally exploits redundancies in the data set, the latter reduces the cost of wavefield simulations by reducing the effective dimension of the numerical mesh. As a consequence, the average cost of an iteration in this inversion is only around 0.62% of an iteration that uses the complete data set with a standard cubed-sphere-type mesh. We calculated 3D synthetic seismograms using a graphics processing unit-accelerated spectral-element wave propagation solver, accommodating the effects of anelasticity, topography, bathymetry, ocean loading, and ellipticity. For a diverse range of global wavepaths, REVEAL predicts complete three-component seismograms at 33 s period that have not been included in the inversion. This generalization to unseen data suggests applications of REVEAL in event location and characterization, as well as in ground-motion modeling.
Resources
- Model as Salvus (spectral-element) mesh file (hdf5) plus xdmf file for ParaView: Download download (4 GB)
- Model as netCDF file: Download download (400 MB)
- Synthetic benchmark dataset: To enable an easy assessment of REVEAL's ability to explain observed 3-component seismograms, we provide a synthetic dataset computed with REVEAL for 22 selected, globally distributed earthquakes. It has been computed using Download Salvus (PDF, 6.3 MB) and can be accessed on external page Zenodo.
Publications
Download REVEAL: A global full-waveform inversion model (PDF, 21.5 MB) (Thrastarson et al., BSSA 2024)
Download Data-adaptive global full-waveform inversion (PDF, 22.8 MB) (Thrastarson et al., GJI 2022)
Download Accelerating numerical wave propagation by wavefield adapted meshes. Part II: full-waveform inversion (PDF, 11.6 MB) (Thrastarson et al., GJI 2020)
Download Accelerated full-waveform inversion using dynamic mini-batches (PDF, 4.6 MB) (van Herwaarden et al., GJI 2020)
FWI of the African Plate
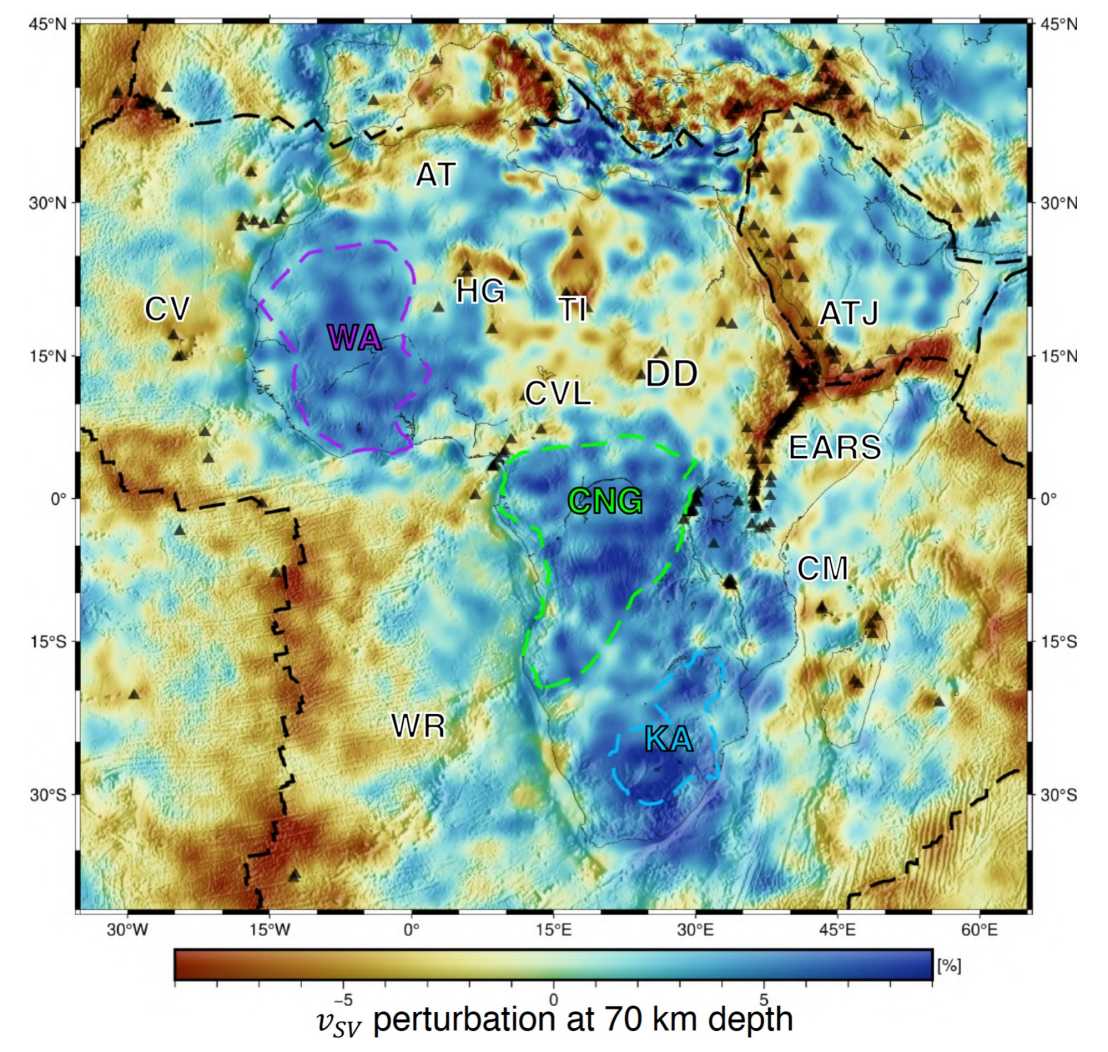
This full seismic waveform inversion of the African Plate was constructed using the combination of spectral-element wavefield simulations, adjoint techniques and stochastic mini-batch optimisation. We performed 130 iterations and invert data from 397 unique earthquakes and 184,356 unique source-receiver pairs. The minimum period is 35 s. We clearly image tectonic features such as the Afar triple junction. Particularly interesting are the low-velocity zones below the Hoggar, Aïr, and Tibesti Mountains, pronounced more than in earlier works. Finally, we introduce a new strategy to assess model uncertainty. We deliberately perturb the final model, perform additional mini-batch iterations, and compare the result with the original final model. This test uses actual seismic data instead of artificially generated synthetic data and requires no assumptions about the linearity of the inverse problem.
Resources
Publications
- external page Full-waveform tomography of the African Plate (van Herwaarden et al., JGR 2023)
Long-wavelength Earth Model (LOWE)
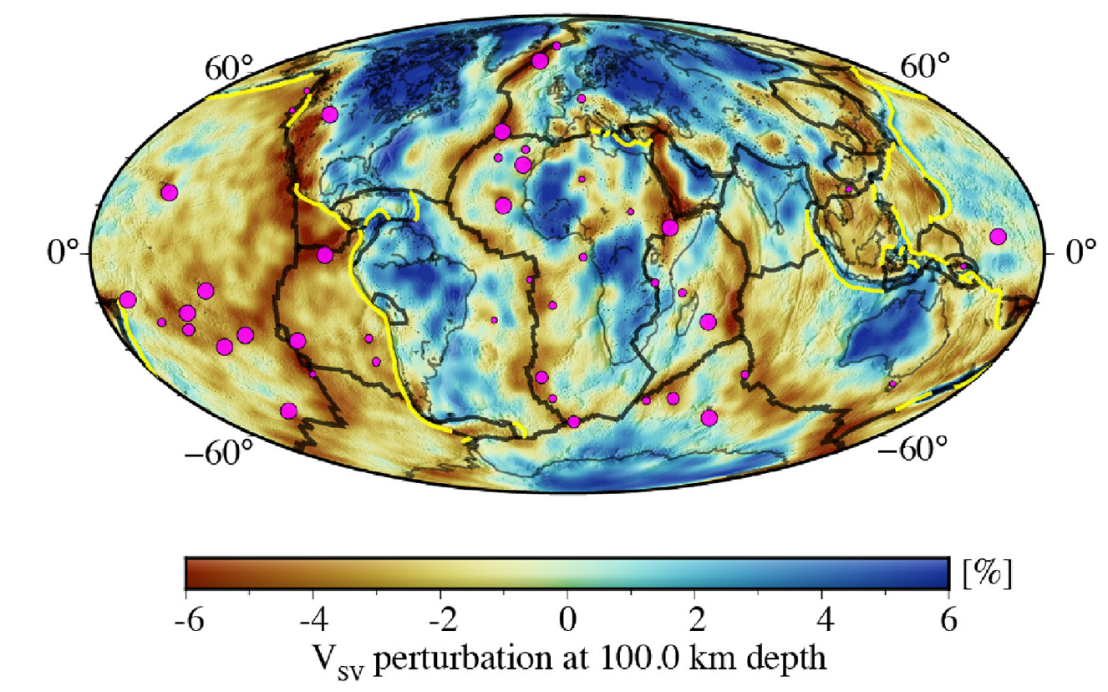
The LOng-Wavelength Earth model (LOWE) is a whole-Earth model of radially anisotropic seismic structure. It has been constructed using full-waveform inversion with wavefield-adapted meshes. Working at periods between 100 - 200 s, it assimilates complete three-component seismic waveforms from 1179 earthquakes.
Resources
The model can be downloaded in two different formats:
- NetCDF for use in the external page IRIS EMC (here)
- HDF5 for use in Salvus simulations (here)
Publications
- external page Data-adaptive global full-waveform inversion (Thrastarson et al., GJI 2022)
- external page Accelerating numerical wave propagation by wavefield adapted meshes. Part II: full-waveform inversion (Thrastarson et al., 2020)
Collaborative Seismic Earth Model: Generation 1
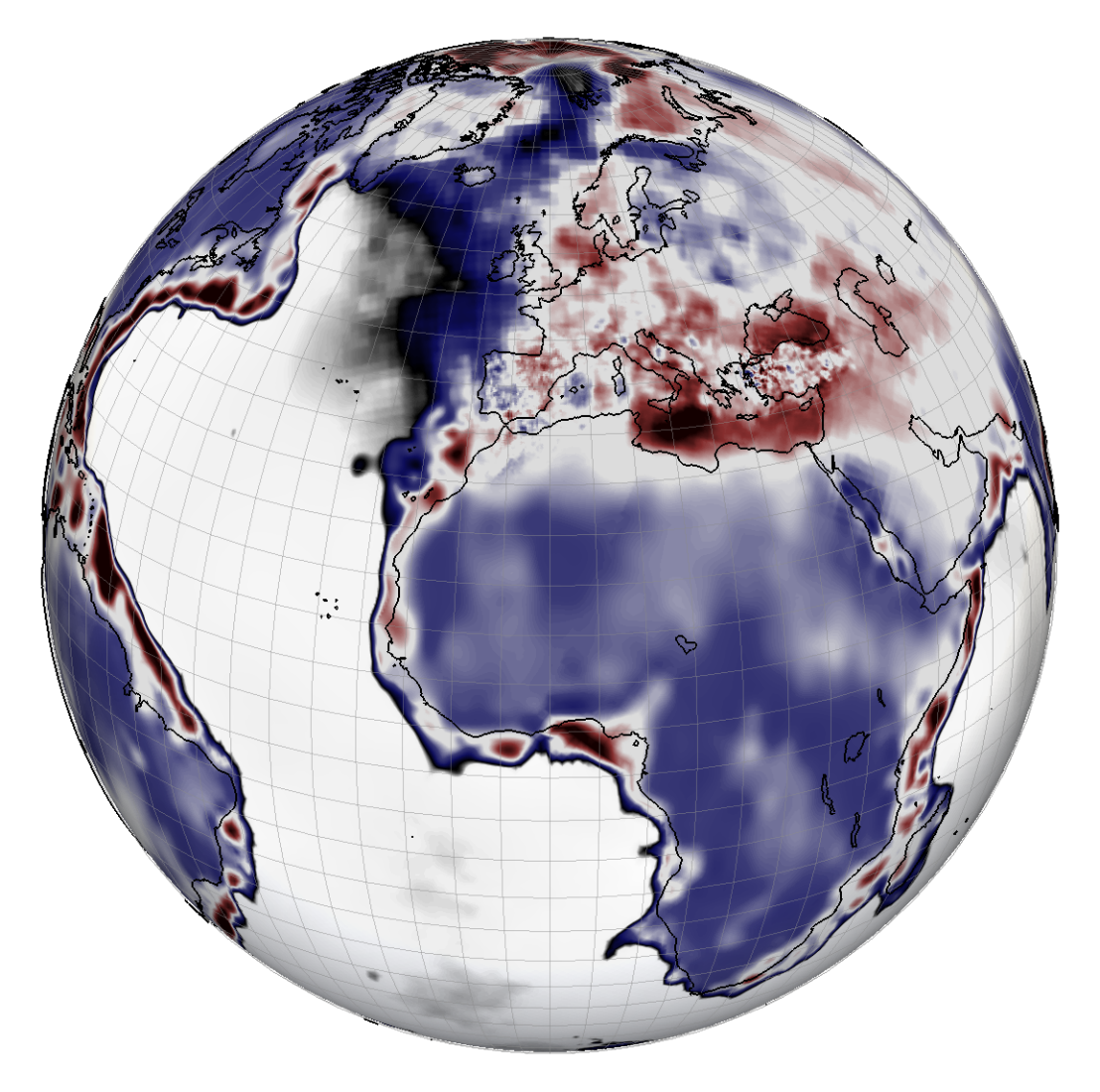
The first-generation Collaborative Seismic Earth Model (CSEM) can be downloaded most easily from the website of the external page IRIS EMC. The second-generation CSEM is now also available.
Publications
EastGRIP Firn Model
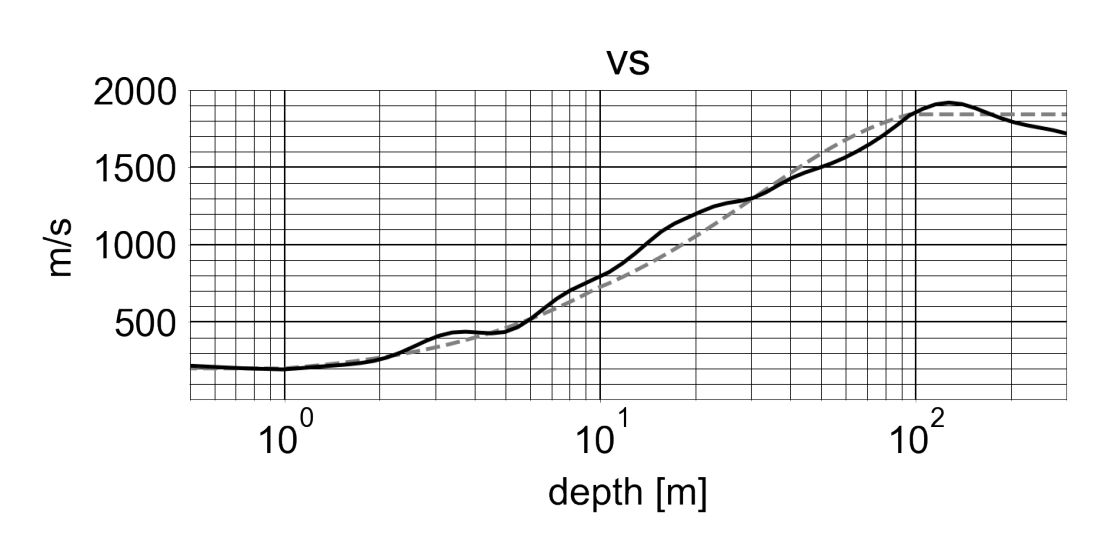
The external page EastGRIP firn model has been derived using Backus-Gilbert inversion of multi-mode dispersion data. These data have been recorded with a 3 km long DAS cable during the landing of a C-130 Hercules near the EastGRIP camp. Field work impressions including the airplane landing can be found on our external page YouTube Channel.
Resources
- Download Raw DAS data and code for data analysis (visualisation, f-k analysis and dispersion curves) (ZIP, 65.7 MB)
- Download Code for Backus-Gilbert inversion, including a suite of possible models (ZIP, 4 MB)
Publications
- external page Fiber-optic airplane seismology on the Northeast Greenland Ice Stream (Fichtner et al., TSR 2023)
EastGRIP Ice Sheet Seismic Model
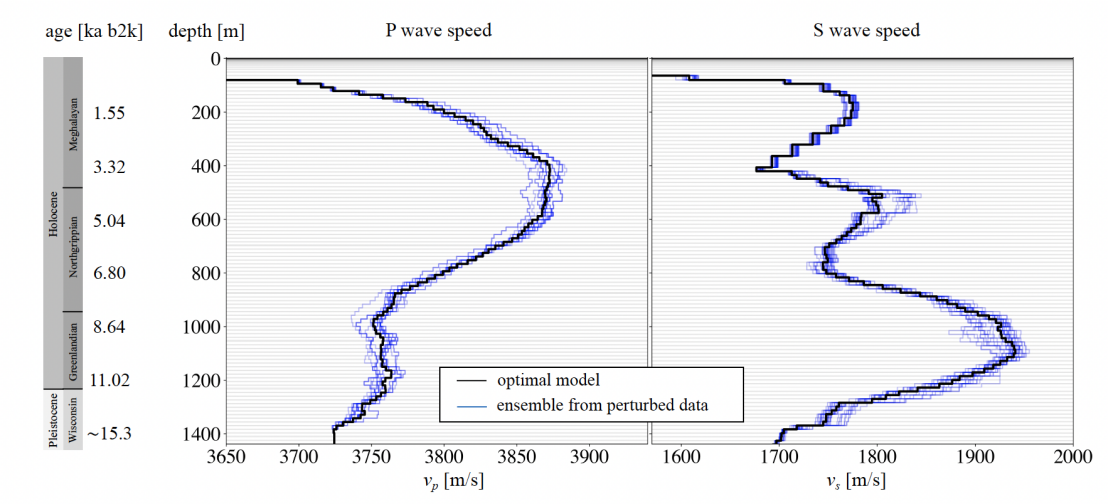
The P and S wave speed model of the Northeast Greenland Ice Sheet near the external page EastGRIP drill site has been computed by nonlinear traveltime inversion of active-shot seismic data recorded within the EastGRIP borehole. For the recordings, we lowered a fibre-optic cable 1'500 m into the borehole and recorded strain rate using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS). Field work impressions can be found on the Yexternal page ouTube channel of our group.
Resources
The active-shot seismic DAS data are freely available here.
The ensmble of acceptable P and S wave speed models can be found here.
Seismic ambient noise source maps
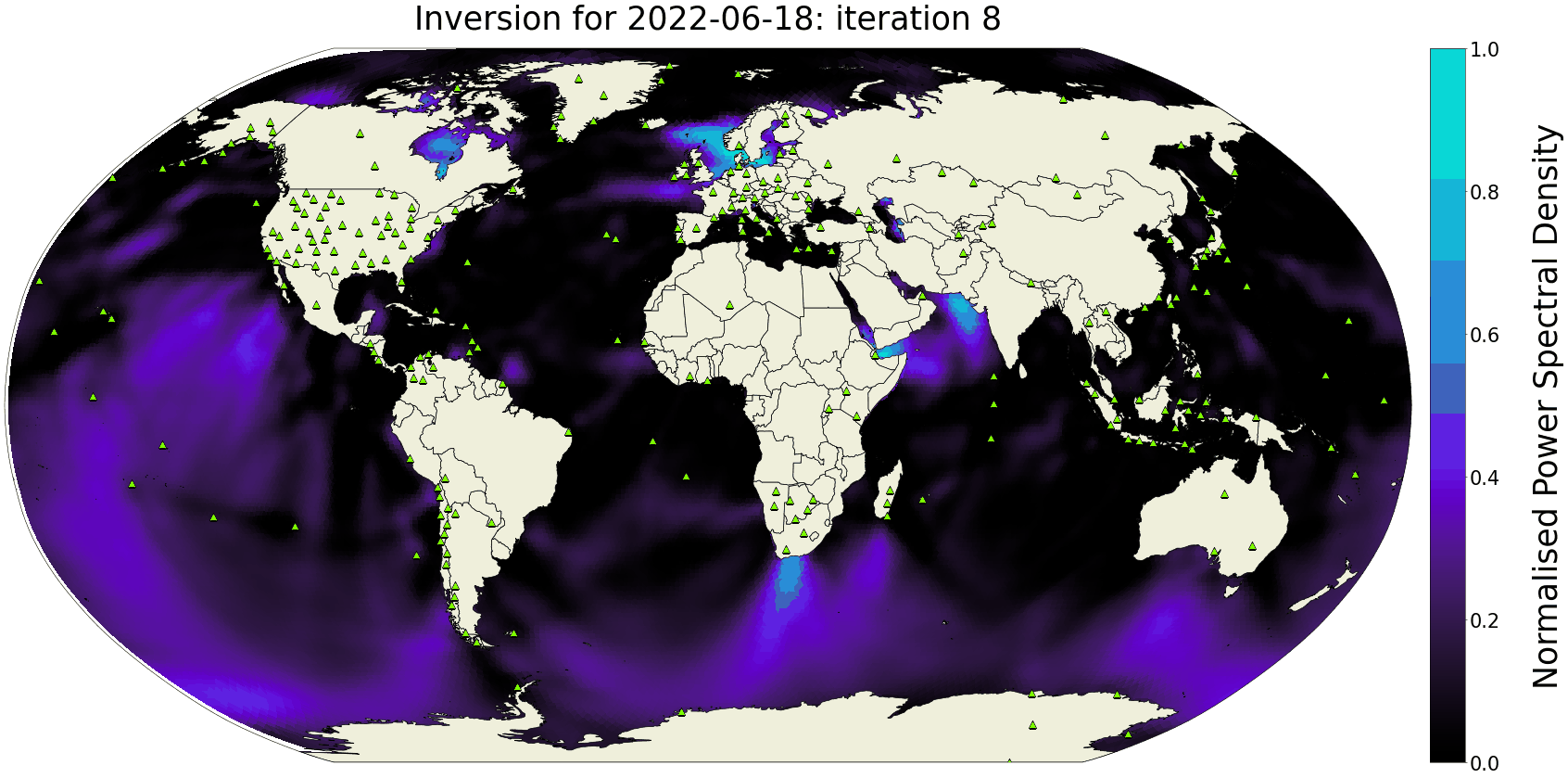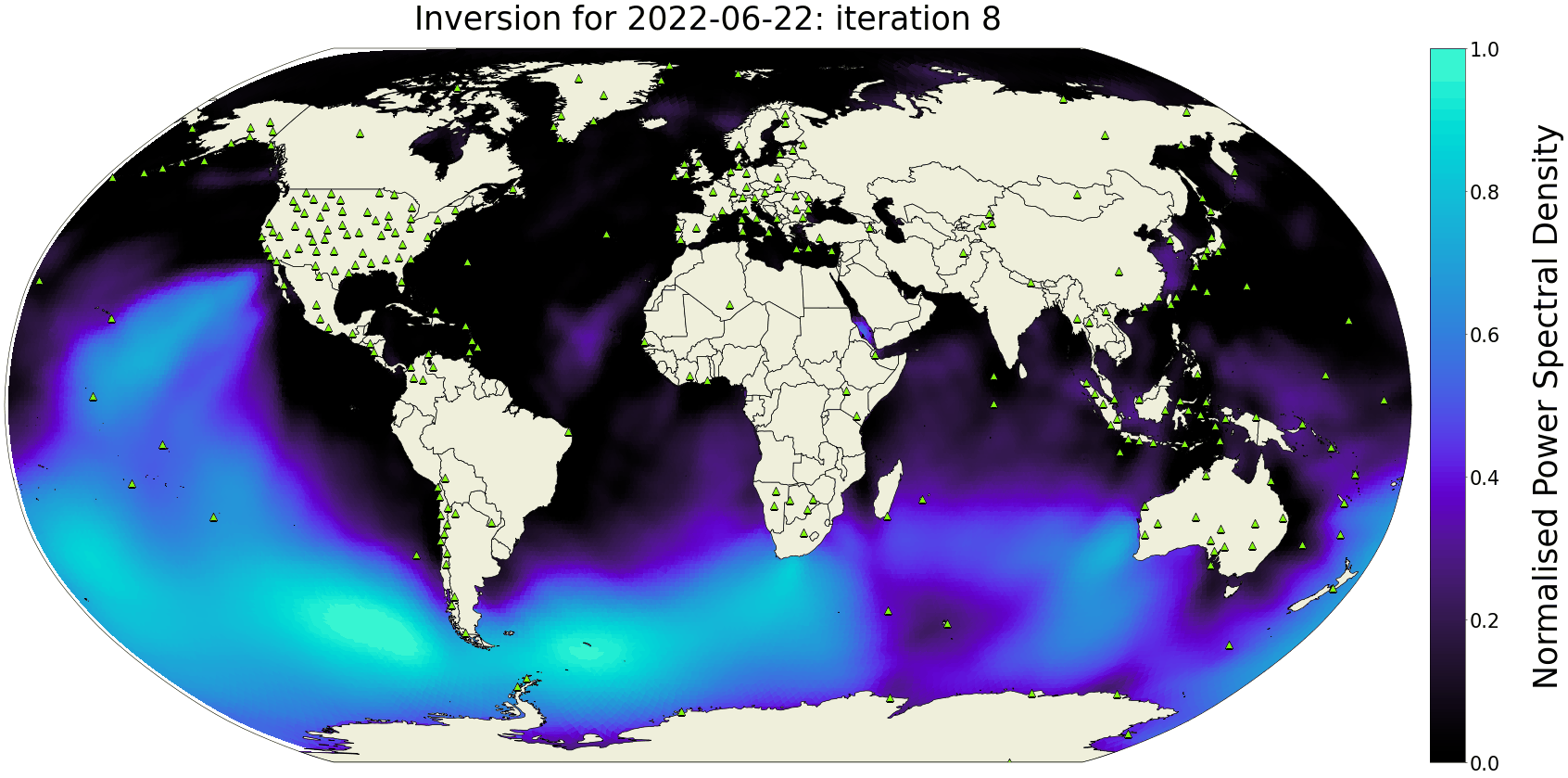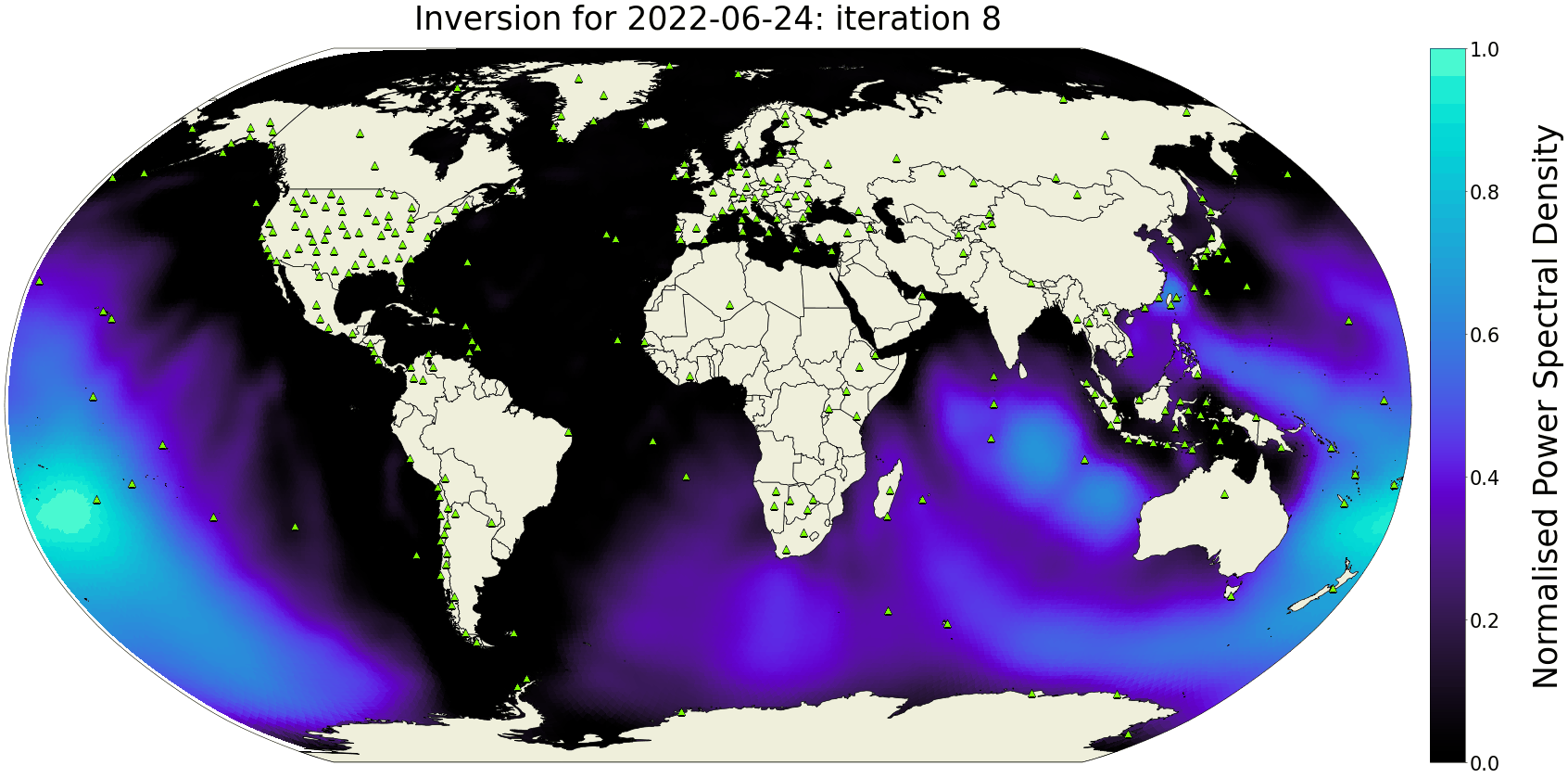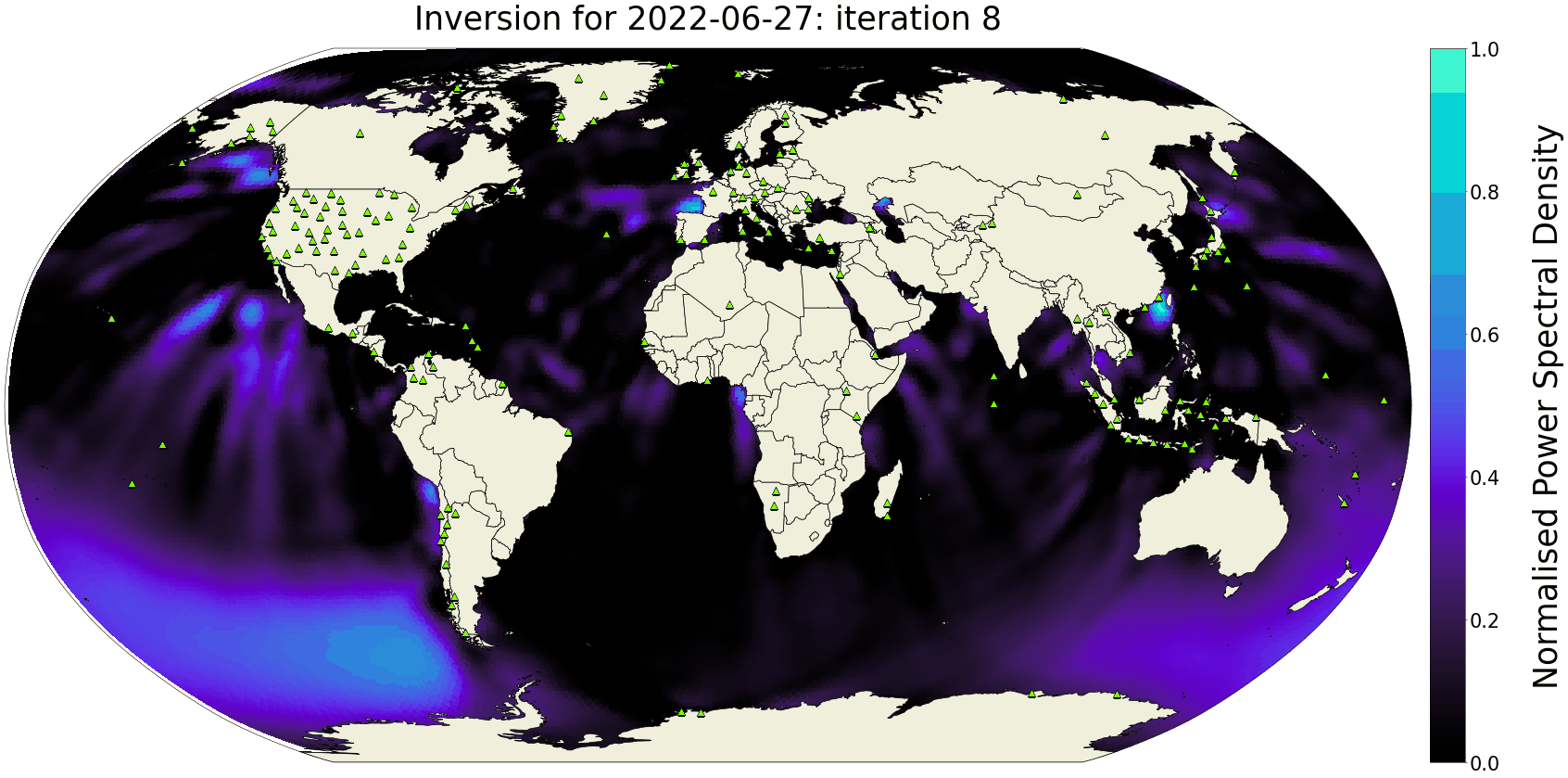
The Seismic Ambient Noise Source maps (SANS) are daily global models of the power-spectral density distribution of microseismic noise sources in the oceans. Using spectral-element wavefield simulations and asymmetry measurements on noise correlations, these maps are computed every day, thereby providing a snapshot of interactions between atmosphere, oceans and the solid Earth with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Resources
The noise source models can be downloaded from the SANS website.
Publications
Frequency-dependent hum sources
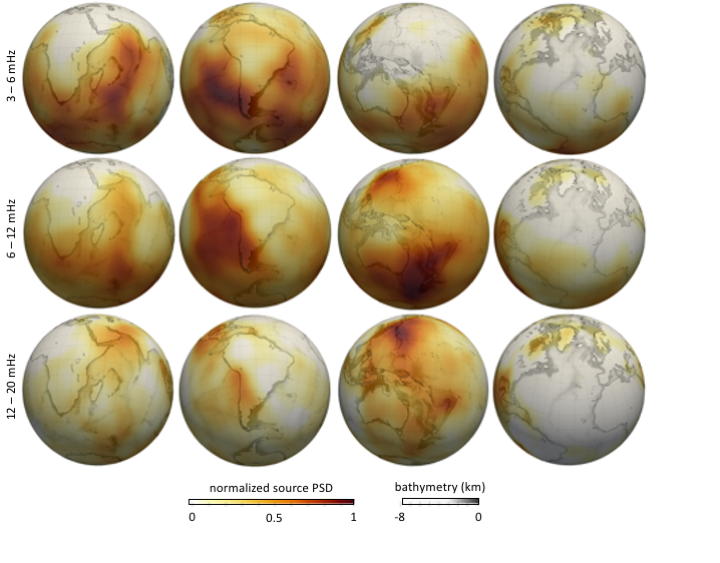
The frequency-dependent hum source model provides the distribution of the power-spectral density distribution of forces at the Earth's surface that excite low-frequency ambient seismic noise.
Resources
The complete model in vtk format can be downloaded Download here.
Publications